目录
Redis获取锁
首先了解下Redisson,获取RLock? RedissionLock
?? public RLock getLock(String name) {
? ? ? ? return new RedissonLock(connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
? ? }? ?//公平锁
? ? public RLock getFairLock(String name) {
? ? ? ? return new RedissonFairLock(connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
? ? }
? ? //读写锁
? ? public RReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock(String name) {
? ? ? ? return new RedissonReadWriteLock(connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
? ? }
加锁操作
?public void lock() {? ? ??
? try {
? ? ? ? ? ? lockInterruptibly();
? ? ? ? } catch (InterruptedException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
? public void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) {
? ? ? ? try {
? ? ? ? ? ? lockInterruptibly(leaseTime, unit);
? ? ? ? } catch (InterruptedException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
首先解析下Lock()方法,该方法不传递参数,主要方法?lockInterruptibly();下面进入该方法查看
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException { lockInterruptibly(-1, null); }public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit)参数?leaseTime 持有锁的时长
参数unit 时间单位
lockInterruptibly
接着开始解析lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit)方法
?public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
? ? ? ? //拿到线程Id 当面获取锁的线程唯一的
? ? ? ? long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
? ? ? ? //得到锁的有效时长
? ? ? ? Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
? ? ? ? // lock acquired
? ? ? ? if (ttl == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? return;
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? //订阅 开启异步线程去监听
? ? ? ? RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
? ? ? ? commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);? ? ? ? try {
? ? ? ? ? //循环直到锁失效 /释放
? ? ? ? ? ? while (true) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? // lock acquired
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? if (ttl == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? break;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? // waiting for message
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? if (ttl >= 0) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? } else {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? } finally {
? ? ? ? ? ?//结束异步线程订阅
? ? ? ? ? ? unsubscribe(future, threadId);
? ? ? ? }
// ? ? ? ?get(lockAsync(leaseTime, unit));
? ? }
分步讲解:
1:进入方法
Long tryAcquire(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId)
private Long tryAcquire(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) { return get(tryAcquireAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId)); }<T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId)该方法就是得到一个RFuture 异步定时任务,后面会定时去更新这个锁的有效时间
protected <V> V get(RFuture<V> future) { return commandExecutor.get(future); }拿到这个定时任务每次更新得到的剩余有效时间
?查看一下?tryAcquireAsync 方法
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {
//对于 Lock()无参而言 leaseTime =-1 会走下一步
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
//拿到获取剩下有效时长的Future
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
return;
}
Long ttlRemaining = future.getNow();
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>(){})会交给netty去执行,开启异步线程
执行监听的时候执行逻辑是这样的?
Long ttlRemaining = future.getNow() 返回null 接着执行scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId)
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout()?
这个是获取看门狗超时时长?
private long lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000; 默认时长3秒也就是默认是持有锁的时间是30秒 ,如果当面线程加锁成功会给加锁setnx? key value expire 30s
public long getLockWatchdogTimeout() { return lockWatchdogTimeout; }
接着看?
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) { //时间转换为毫秒 这里T是Long类型 要get()的结果就是锁的剩余有效时长单位毫秒 internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime); return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command, "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " + "redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + "return nil; " + "end; " + "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " + "redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + "return nil; " + "end; " + "return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId)); }ARGV[1] =?internalLockLeaseTime
ARGV[2]=getLockName(threadId)??
String getLockName(long threadId) { return id + ":" + threadId; }
主要就是去执行下面这段luna脚本的,首选判断redis key是否存在,key就是getName(),也就是你使用锁的时候加锁的名称redission.getLock(lockName),第一个线程加锁肯定是不存在的可以继续操作,也就是set命令执行写操作 value就是getLockName(threadId)? ,然后设置有效时长
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " + "redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + "return nil; " + "end; " + "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " + "redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + "return nil; " + "end; " + "return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()),
如果再往下面看就是执行 下面的逻辑的,这些暂不介绍
public <T, R> RFuture<R> evalWriteAsync(String key, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> evalCommandType, String script, List<Object> keys, Object... params) {
NodeSource source = getNodeSource(key);
return evalAsync(source, false, codec, evalCommandType, script, keys, params);
}
?真正执行的这段luna脚本?eval script args?
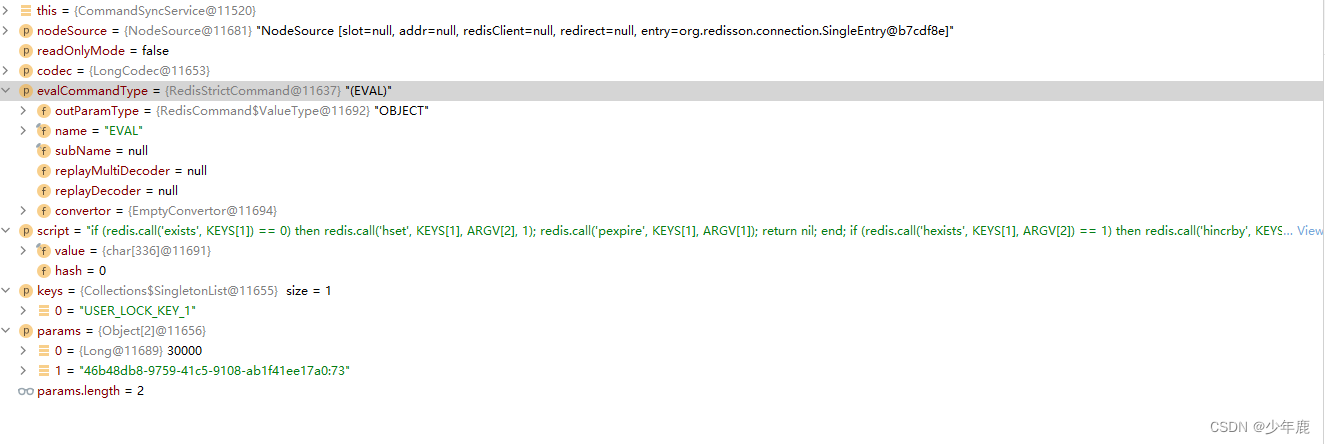
?会在redis里写入key USER_LOCK_KEY_1 value??46b48db8-9759-41c5-9108-ab1f41ee17a0:73?
pexpire??30000
?回到tryAcquireAsync方法,将key value写进redis后会返回一个RFuture,这东西继承了Future
public interface RFuture<V> extends java.util.concurrent.Future<V>, CompletionStage<V>
然后添加线程监听器,监听锁的有效时间是否过时或者锁是否已经被释放
接着看下面这个方法
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(final long threadId)
根据方法名就可以知道,该方法就是重新设置过期时间的,会根据当前的线程Id去获取线程加的锁,去查看锁的有效时间,根据定时任务去每次间隔三分之一的internalLockLeaseTim时间执行一次
?再回到方法
<T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId)?
可以知道获取到ttlRemainingFuture后就会开启监听,启动线程一直去定时刷新锁的剩余时间,直到锁被释放
接着 看lockInterruptibly()方法
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId); commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
?subscriber是redis的消息订阅模式,会执行PublishSubscribe类的方法
public RFuture<E> subscribe(final String entryName, final String channelName, final PublishSubscribeService subscribeService) {
final AtomicReference<Runnable> listenerHolder = new AtomicReference<Runnable>();
final AsyncSemaphore semaphore = subscribeService.getSemaphore(channelName);
final RPromise<E> newPromise = new RedissonPromise<E>() {
@Override
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
return semaphore.remove(listenerHolder.get());
}
};
Runnable listener = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
E entry = entries.get(entryName);
if (entry != null) {
entry.aquire();
semaphore.release();
entry.getPromise().addListener(new TransferListener<E>(newPromise));
return;
}
E value = createEntry(newPromise);
value.aquire();
E oldValue = entries.putIfAbsent(entryName, value);
if (oldValue != null) {
oldValue.aquire();
semaphore.release();
oldValue.getPromise().addListener(new TransferListener<E>(newPromise));
return;
}
RedisPubSubListener<Object> listener = createListener(channelName, value);
subscribeService.subscribe(LongCodec.INSTANCE, channelName, semaphore, listener);
}
};
semaphore.acquire(listener);
listenerHolder.set(listener);
return newPromise;
}
后面就是简单的一个循环,在while循环里面调用tryAcquire 方法 更新锁的有效时间,最后取消订阅
while (true) {
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
break;
}
// waiting for message
if (ttl >= 0) {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
?
unLock
redission.unLock()
public void unlock() {
Boolean opStatus = get(unlockInnerAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId()));
if (opStatus == null) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: "
+ id + " thread-id: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
if (opStatus) {
cancelExpirationRenewal();
}
// Future<Void> future = unlockAsync();
// future.awaitUninterruptibly();
// if (future.isSuccess()) {
// return;
// }
// if (future.cause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
// throw (IllegalMonitorStateException)future.cause();
// }
// throw commandExecutor.convertException(future);
}
执行redis del 语句
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end;" +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.unlockMessage, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
取消定时任务续命锁的有效时间
void cancelExpirationRenewal() { Timeout task = expirationRenewalMap.remove(getEntryName()); if (task != null) { task.cancel(); } }?取消任务取消的是 netty开启的 时间轮定时任务Timer?
HashedWheelTimer 类public boolean cancel() { // only update the state it will be removed from HashedWheelBucket on next tick. if (!compareAndSetState(ST_INIT, ST_CANCELLED)) { return false; } // If a task should be canceled we put this to another queue which will be processed on each tick. // So this means that we will have a GC latency of max. 1 tick duration which is good enough. This way // we can make again use of our MpscLinkedQueue and so minimize the locking / overhead as much as possible. timer.cancelledTimeouts.add(this); return true; }
记住上面在执行 tryAcquireAsync方法的时候,对于leaseTime是否传入值,会走不同的方法,再看下
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {if (leaseTime != -1) { return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG); } RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG); ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>(){ ......????????if (ttlRemaining == null) { ???????? scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId); ????????} ?????} ? } return ttlRemainingFuture; }
如果你使用的是这个方法?
lock.lock(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);是不会启动看门狗后台任务刷新锁的有效时间的为初始值30秒的因为它没走下面的scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId); 方法
通用的道理,对于
lock.tryLock(10,30,TimeUnit.SECONDS); lock.lockInterruptibly(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);这些方法,因为已经传入默认的持有锁的时间,所以是不会走看门狗监听任务去续命锁的时间的
下面的两个方法可以获取看门狗监听任务刷新锁有效时间
lock.lockInterruptibly(); lock.tryLock(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS); 表示多线程下不同线程去强占锁的时候会等待10秒,如果10秒钟没有或得锁,就获取不到,需要等待,如果10秒内能够获取到锁就直接执行,不同于Lock(),这个没有等待时间
