-
这段时间做目标跟踪,用到了DarkLabel 来标注自己的数据集,但是这个软件只有 voc 跟coco格式的输出,没有我想要的OTB格式的输出 ,而且网上这个方面的博客也很少于是打算记录一下
-
DarkLabel 下载地址 https://github.com/darkpgmr/DarkLabel
-
 这里选择 pascal voc 格式
这里选择 pascal voc 格式 -
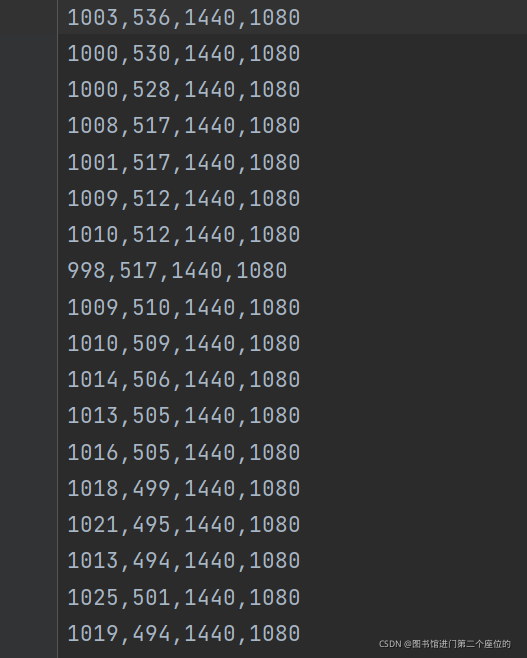
生成的voc标注格式如下


-
然后就是转换的代码
#coding=utf-8
from lxml import etree
import os
def parse_xml_to_dict(xml):
"""
将xml文件解析成字典形式,参考tensorflow的recursive_parse_xml_to_dict
Args:
xml: xml tree obtained by parsing XML file contents using lxml.etree
Returns:
Python dictionary holding XML contents.
"""
if len(xml) == 0: # 遍历到底层,直接返回tag对应的信息
return {xml.tag: xml.text}
result = {}
for child in xml:
child_result = parse_xml_to_dict(child) # 递归遍历标签信息
if child.tag != 'object':
result[child.tag] = child_result[child.tag]
else:
if child.tag not in result: # 因为object可能有多个,所以需要放入列表里
result[child.tag] = []
result[child.tag].append(child_result[child.tag])
return {xml.tag: result}
a = sorted([i for i in os.listdir(r'你自己的\gt_xml')])
for path in a:
with open(r'你自己的/gt_xml' + '/' + str(path)) as fid:
xml_str = fid.read()
xml = etree.fromstring(xml_str) #原文档根节点
data = parse_xml_to_dict(xml)["annotation"]
box = []
for obj in data["object"]:
xmin = int(obj["bndbox"]["xmin"])
xmax = int(obj["bndbox"]["xmax"])
ymin = int(obj["bndbox"]["ymin"])
ymax = int(obj["bndbox"]["ymax"])
data_width = xmax - xmin
data_height = ymax - ymin
box.append([xmin,ymin,data_width,data_height])
write_line = "%d,%d,%d,%d\n" %(box[0][0],box[0][1],box[0][2], box[0][3])
f = open("t.txt", "a+")
f.write(write_line)
f.close()
- 效果